News
Justice Delayed: Billionaire Candidate’s Coal Companies Owe $15M in Taxes, Fines
By: Benny Becker | Ohio Valley ReSource
Posted on:
The Democratic candidate for governor in West Virginia has never held public office. Jim Justice is instead running on his record as a businessman. He runs coal mines, farms, and a luxury resort, and according to Forbes, he’s also the wealthiest person in the state, worth $1.56 billion.
A review of records by NPR and the Ohio Valley ReSource shows that his coal companies owe more than $12 million in overdue county, state, and federal taxes, as well as over $2 million for mine safety violations. Add a lengthy list of environmental violations and damaged mine sites, and a pattern emerges: Justice’s business liabilities have in many cases become public liabilities, and the costs often fall hardest on already cash-strapped communities in the Appalachian coalfields. [Story continues below graphic]
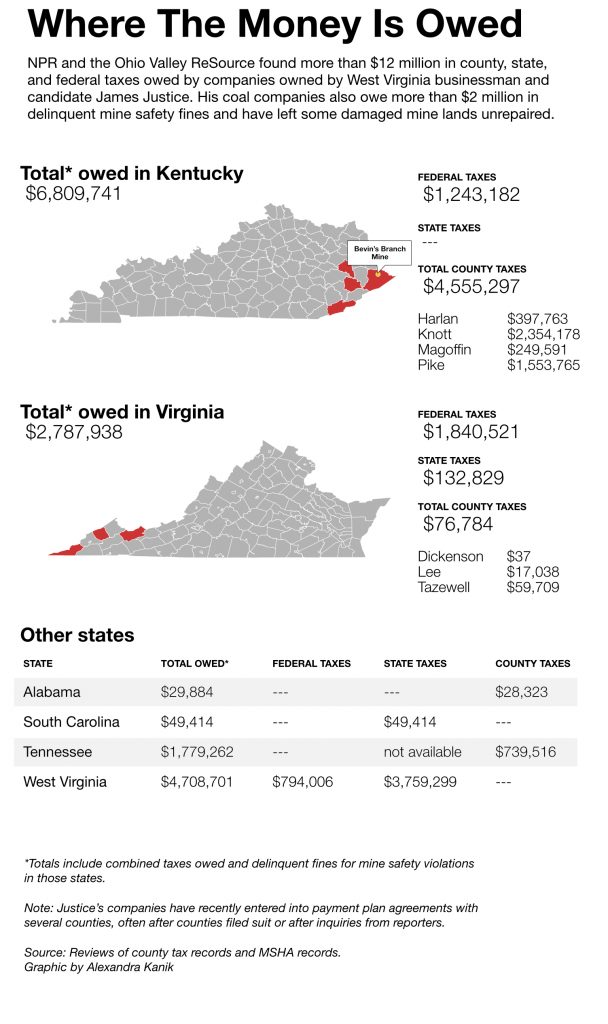 Alexandra Kanik | Ohio Valley ReSource
Alexandra Kanik | Ohio Valley ReSourceThe review by NPR, the ReSource and its partner station West Virginia Public Broadcasting provides the first comprehensive accounting of these debts and delinquencies. Some of Justice’s problems with taxes, mine safety and environmental violations have been reported previously, raising criticism of the billionaire candidate.
For example, in April the Charleston Gazette-Mail reported that Jim Justice owed at least $3.9 million in overdue property taxes to six West Virginia counties. Justice quickly committed to paying all those taxes.
“Every single tax obligation that I have in West Virginia will be paid before the end of the month of April,” Justice said at the time.
That month, Justice did pay down a lot of the property taxes he owed to counties in West Virginia, but that covered just a fraction of his total delinquent tax bill. He still owes $3.7 million dollars in West Virginia state taxes. His companies also owe more than $3 million in overdue federal taxes, and in counties outside of West Virginia, Justice still owes large amounts of property taxes, mainly in the coalfields of eastern Kentucky.
“A Huge Burden”
Knott County has been hit hard by the coal industry’s decline. The county budget is now half what it was just seven years ago. Knott County is also owed owed more than $2.3 million by Justice, the most of any county.

Knott County Judge-Executive Zach Weinberg described Justice’s company as “a repeat offender” and explained that the county has already won two lawsuits against Justice’s company to force payment of back taxes.
“Every dollar that somebody doesn’t pay puts a huge burden on the county,” Weinberg said.

The situation isn’t unique to Knott County. Justice’s companies owe another $3 million to other counties across Appalachia. In Tazewell County, Virginia, Treasurer David Larimer seized mining equipment to force a payment. He described walking around the mine’s gravel driveway on a snowy day, using scotch tape to attach seizure orders to every piece of equipment he saw.
“Continuous miners, ventilation systems, computers in the office,” Larimer said, “we put notice on there that it was a felony to move it.”

“We Lost Everything”
As NPR has reported, Justice’s coal companies owe $2 million in outstanding mine safety fines, the most of any mining operation in the country. His companies also have a history of environmental problems. Justice recently reached a settlement with state and federal agencies for water pollution violations in five states. The settlement calls for $5 million worth of fixes, and $900,000 in fines.
In Kentucky, Justice companies had already racked up more than five hundred violations and over $4 million in fines for failing to restore land that they’d mined. The state negotiated multiple rounds of agreed orders with Justice, but his companies weren’t living up to them, so the state took Justice to court. There’s been steady progress since then, but Justice’s companies still have a lot more reclamation work to do, and nearby residents say some unreclaimed mines have already caused serious damage.
Click here to explore the interactive timeline >>
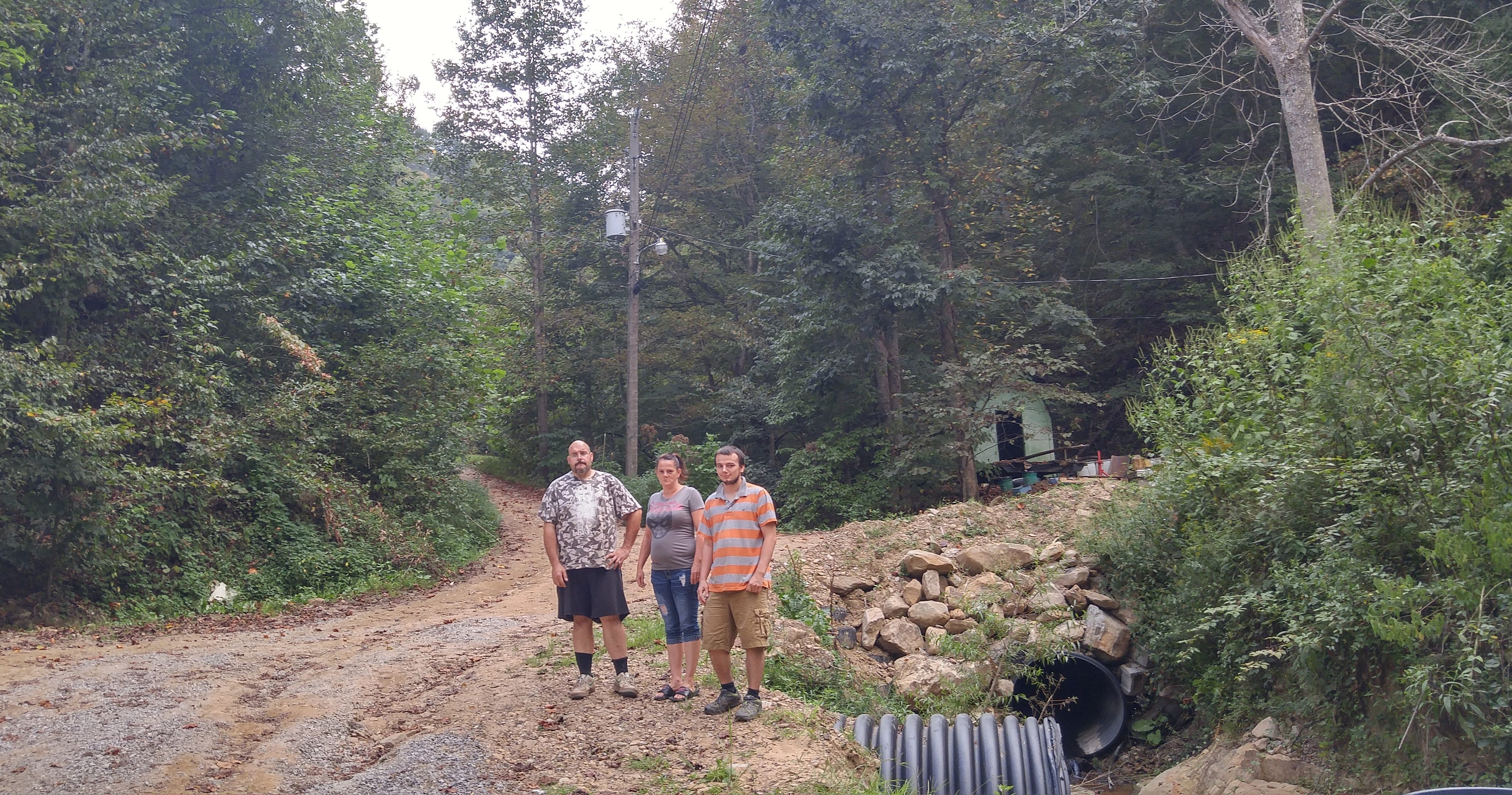
Bevin’s Branch is a Justice-owned surface mine in Pike County, Kentucky. Justice’s company had committed to reclaim the site by July 2015, but little had been done by the night of June 3rd, 2016, when a heavy rain fell on the strip mine. The runoff breached a diversion ditch and sent a torrent of mud and debris flooding down the mountain.
Chad Keene said the scene looked “like a bomb went off” at the bottom of the slope where he lives.
“All you could see was a wall of water, rock, trees, dirt and everything that had washed from the mine site,” he said.
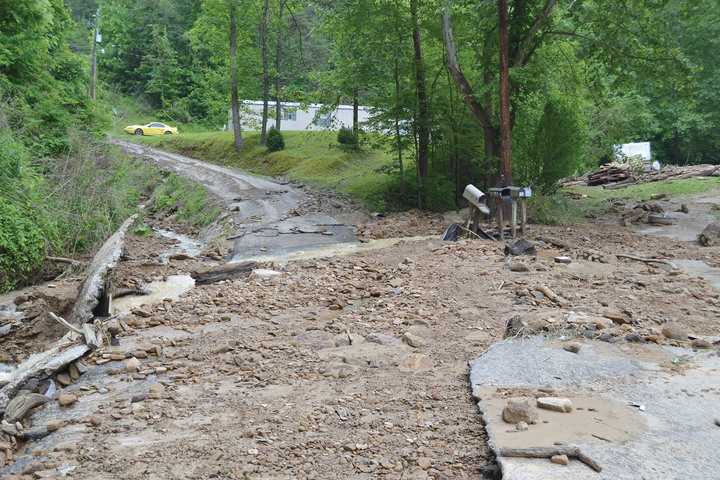

Keene’s driveway was washed out by the flood, as was the road in front of his house. Keene, his girlfriend Mollie Smith, and her son Toby Daniels had no way out, and neither did any of their neighbors up the road. Their water was cut off and they didn’t have a lot of food, so that made the situation even scarier. Smith said the water hadn’t gone down by daylight, and that it was another couple of days before the road was clear enough for a car to get through.
A second stream of mud and debris rushed down the mountain that night. Laura and Elvis Thacker said it flooded their property just ten minutes after the rain started, coming so fast that several of their cats drowned.
They didn’t realize what was happening until they decided to check out why the storm sounded a little strange. They headed toward the back patio and saw mud piled more than a foot high against the glass door. It wasn’t until the sun came up the next morning that they saw the massive tangle of rocks and logs just uphill from their house, stopped by a trailer and their garage, which were nudged downhill in the process.
Their house wasn’t moved, but the mud knocked out support blocks, water seeped through the walls, and now mold has set in. Their contractor estimated the damages at $148,000.
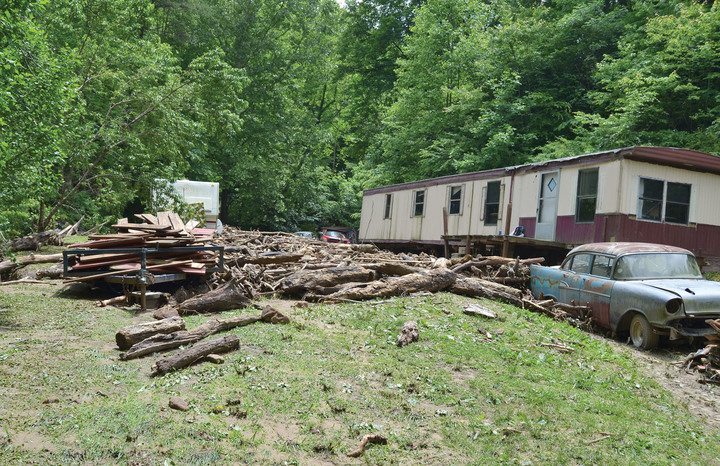

The Thackers said they’d been offered some money by Justice’s company, but not even enough to buy a cheap double-wide trailer, much less to cover the cost of demolishing their ruined home and replacing everything else they lost in the flood.
The Thackers said it was especially hard to stomach the loss because they’d only recently achieved financial stability. After Elvis lost his coal job seven years ago, they lost a car and a truck, and for years they worked two jobs apiece, trying to stay afloat.
“We’ve lost everything,” Laura Thacker said, “we’re going to have to start all over.”

The couple is now talking to a lawyer, trying to get Justice and his company to take responsibility and pay for the damage. The company fixed the ditch that breached and caused the flood, but there are still outstanding reclamation issues on that mine site, and it’s still a cause for concern.
Many of those affected by the flood described lasting emotional trauma. Chad Keene said that he and Mollie Smith don’t sleep when it rains. If it’s raining, they take turns watching the creek just in case it happens again.
“You always worry when the next one’s gonna break,” Smith said, “and you always just live in fear.”

Better Than Bankruptcy?
Jim Justice and his team didn’t respond to our interview requests, but back in April, Justice responded to earlier criticism during a Democratic primary debate in the governor’s race.
“Jim Justice has never bankrupted any company,” he said. “It would’ve been an easy way. Just shut the doors. Let everybody get stuck. I didn’t do it. I promise you that every single obligation that I ever have will be fulfilled.”
Justice’s attorney, Billy Shelton, echoed this argument in a written response last month to questions submitted by NPR about Justice’s unpaid mine safety fines.
“[T]he Justice Companies are being responsible and following the agreed upon payment plan,” Shelton wrote. “To imply anything beyond that is purely for political reasons and ignores the facts.”
Back in Knott County, Judge Weinberg said he understands how delayed payments could be better than bankruptcy. But he said it’s harder to accept that explanation coming from a billionaire, and doesn’t count for much until Knott County actually gets its money.
“If they eventually pay it that’s probably true,” Weinberg said, “but if they don’t pay it, it’s not better at all.”
After inquiries from reporters and legal action by some county officials, Justice’s companies have recently started making some payments on several of their long-overdue tax bills, including in Knott County. It’s a start, but there’s still a lot of money owed, and in many cases, damage has already been done. As the saying goes, justice delayed is justice denied.


