News
The Big Latch: Rising Breast-feeding Rates Could Boost Region’s Health
By: Mary Meehan | Ohio Valley ReSource
Posted on:
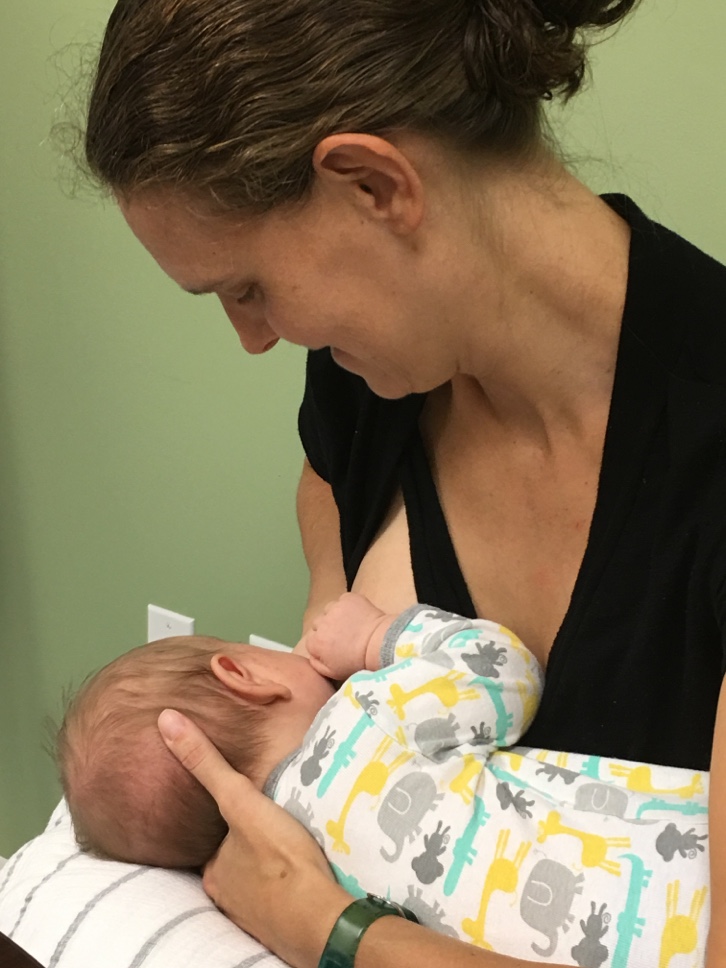
Edwin Hall is dressed in a footed onsie covered in the pastel shades of monkeys and hippos. Although Edwin’s just seven weeks old he already tells his mom when he’s hungry with a sharp and persistent yelp.
Soon after he gets her attention, Edwin is practicing his sucking technique. His mom, Sarah, with the dazed look of the sleep deprived, talks with a La Leche League volunteer at the Madison County, Kentucky, Health Department about some breast-feeding challenges.
Advocates like to say that breast-feeding is a completely natural act but it does take some practice. Support from volunteers at the La Leche League or other lactation specialists can help nursing mothers persist if they have problems.
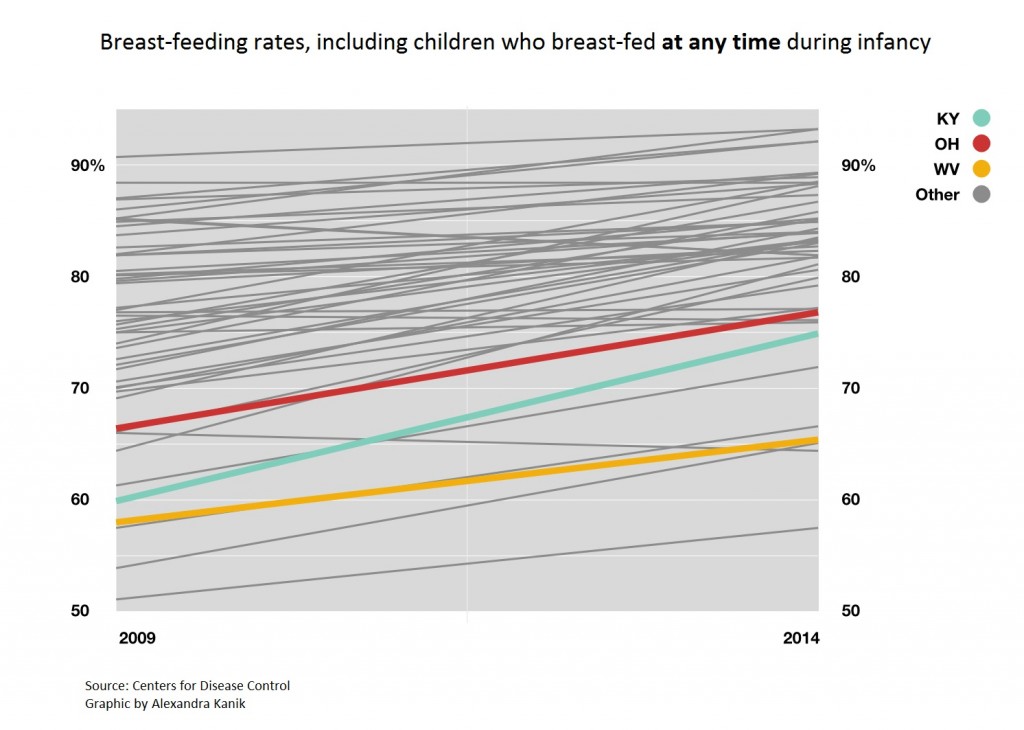
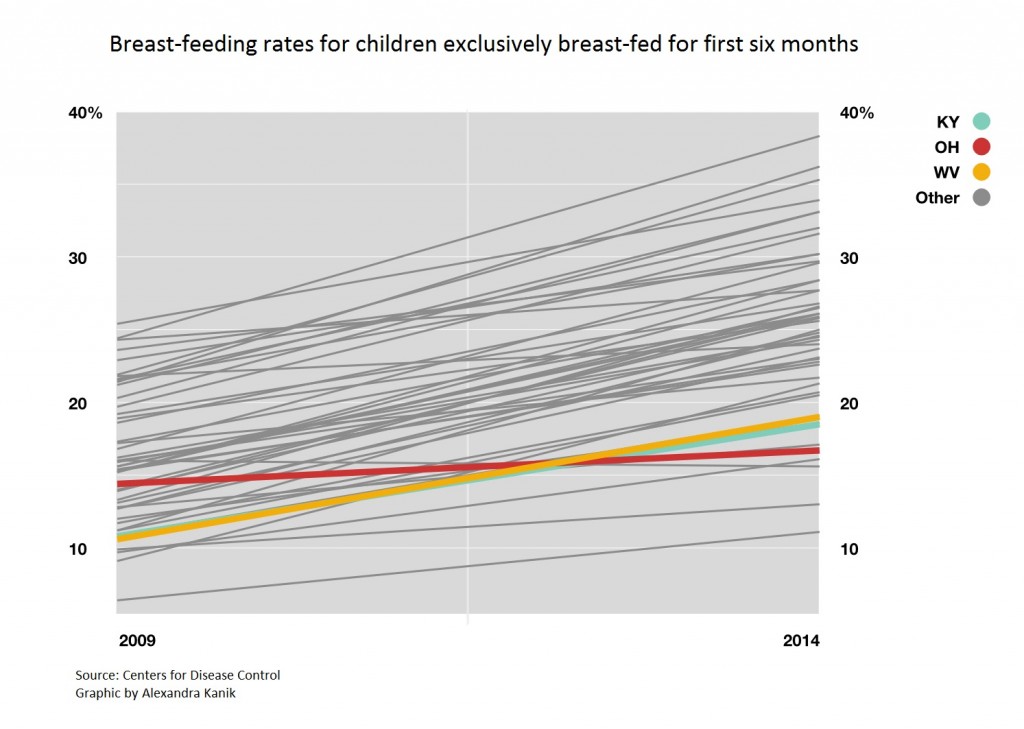
That kind of support is especially important in Kentucky, Ohio, and West Virginia, where breast-feeding rates lag behind the national average. Health researchers say that is beginning to change as an increasing amount of research points to health benefits from breast-feeding that can extend into adulthood.

Starting Conversations
La Leche League volunteer Ashley Kester is herself a mom. She has two boys and another child on the way. When she had her first baby, she said, she was almost clueless about the health benefits of breast-feeding. She said she can see a difference in the health of her second child.
She’s a nurse by profession, but it was through her work as a volunteer that she learned that a lot of new moms don’t know who to ask for help.
“Our moms in this generation haven’t really been exposed to a lot of breast-feeding, they may not have been breast-fed,” she said. “They don’t really know what it looks like and it can seem like a kind of an odd thing to do because formula feeding seems to be the norm.”
Breast-feeding rates vary across the country, with the highest rates in the western states and the lowest in the south. The Ohio Valley states rank among the lowest despite steady increases in breast-feeding in recent years.
Kester said educational and socioeconomic differences play a role. Women who have higher levels of education, and higher income levels, tend to also have higher levels of breast-feeding.
She said a lot of the moms she works with have challenges, such as hourly jobs with short breaks, that make breast-feeding difficult. And she said talking about breast-feeding can be difficult.
Popular culture uses breasts for everything from selling beer to hawking cars, she said, but there is little talk about their biological purpose, nourishing newborns. That can make for some awkward initial conversations with new moms. There is often no exposure to the process before the baby is born.
Edwin’s mom, Sarah Hall, who is a agriculture professor at Berea College, was determined to breast-feed. But she said it’s been hard.
Her son had trouble latching on which made her nipples raw and made breastfeeding extremely painful. She said since she hadn’t breast-fed before she didn’t know it wasn’t suppose to feel that bad.
She also said just finding the right person to talk to about breast-feeding can be difficult, especially as a new mom juggling a whole new set of responsibilities on top of healing from the birth. That’s why she’s made getting to the La Leche League monthly meeting a priority.
Health Benefits
Dr. Ilana Azulay Chertok is a professor and associate director of nursing research and scholarship at the Ohio University. She is currently focusing on breast-feeding and maternal and infant health in Appalachia. Chertok said there are lots of factors to consider when looking at who does and doesn’t breast-feed.
“It could be related to population, location, culture as well as messages from the local health care providers,” she said. Attitudes toward breast-feeding can vary from community to community but the basics of health improvements for breast-fed babies is becoming better understood among moms.

Breast-feeding has been shown to reduce ear infections, respiratory illness, and bouts of diarrhea in infants, she said. A small study recently showed a slight but significant decrease in the level of obesity in breast-fed children in Kentucky and a number of other states. That study focused on families receiving food assistance through the WIC, or Women, Infants and Children, program.
Chertok said a study of 14,000 people across eight European countries also supported the idea that breast-feeding helped curb childhood obesity.
Chertok said breast-fed babies seem to develop a better biological signal to make them feel full.
“Once a baby already learns their satiety cures, which is obviously they learn very early that can affect them for a lifetime,”she said.
She says researchers are finding health benefits can stretch to adulthood as well. She explains breast-feeding helps create a healthy microbiome, or the many different bacterial species that makeup our digestive system.
That, she said, “affords us protection against autoimmune diseases such as diabetes.”
“Human milk has these bio-active components that help guide infants’ immunologic and metabolic development,” she said. “It really positively influences metabolic health.”
One Latch At A Time
Chertok said there have been lots of efforts to try to promote breast-feeding and the numbers show progress. In Kentucky, for example there was a 15 percentage point increase in breast-feeding between 2009 and 2014.
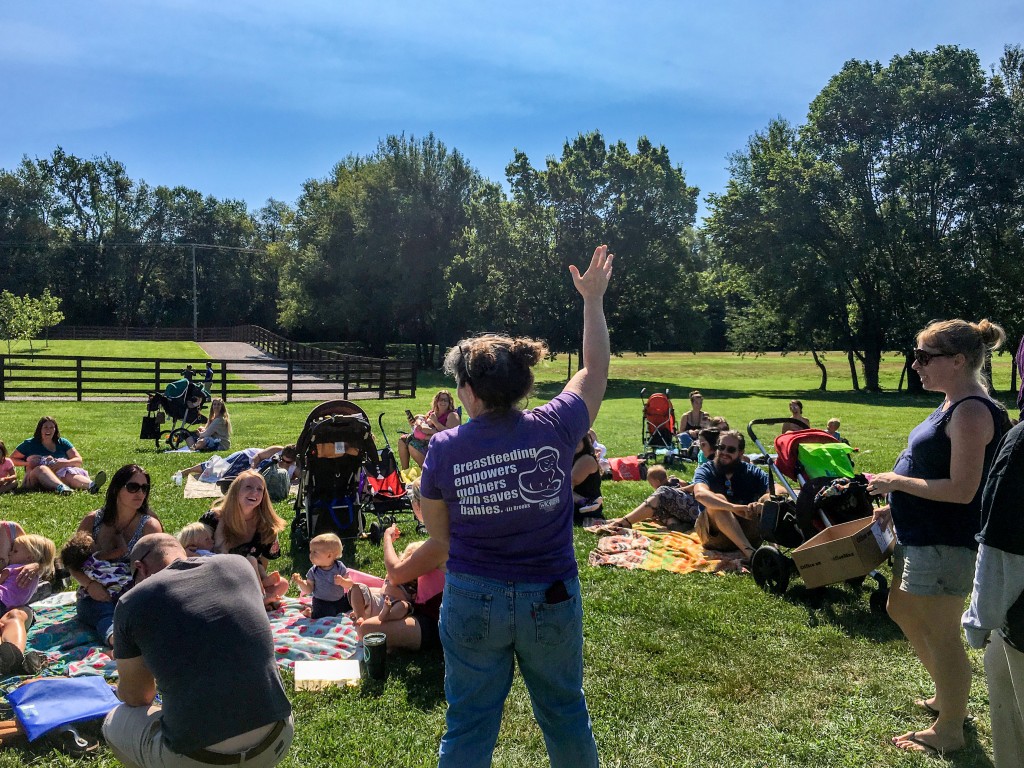
Earlier this year, some 50,000 women at synchronized events around the world simultaneously began nursing during the annual “Big Latch On.” Lexington lactation expert Doraine Bailey led the countdown for dozens of women sitting in a grassy park, breasts and infants at the ready.
She stood, hand in the air, and gave the countdown.
“Ready, set, latch!”
What followed next was mostly the quiet of babies nursing.

Bailey works for the Lexington-Fayette County Health Department. She said the increased support for nursing mothers through lactation consultants, health departments and volunteers means breast-feeding rates throughout the region are only going to continue to improve.
High-quality information is more readily accessible to mothers, she said. Even “Dr. Google” can play a positive role and more connections are possible via social media groups.
“We’ve just spent the last generation really improving the quality and quantity of the research that was done to really understand the breast,” she said. “It is not as mysterious as we’ve been making it.”
At the “Latch On,” mom Katie Saltz helped her daughter, Gwen, crack the code. After a few seconds, Gwen, emits a loud “gulp” followed by praise from Mom.
“She’s a pretty good eater. I’ve been blessed to have three kids that are good latchers,” she said.
And Bailey said that’s how the health benefits from breast-feeding will continue to grow: One Mom and baby, one latch-on at a time.